WEB TUTORIAL - Group Theory
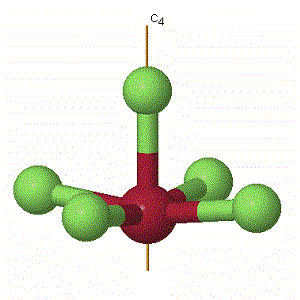
Cn - Proper axis of rotation - with n being the order of the axis. This symmetry element is present whenever a rotation through an angle of 360°/n results in an equivalent configuration. The orientation of the molecule is defined by this axis; the rotational axis with the highest order (n) is identified as vertical.
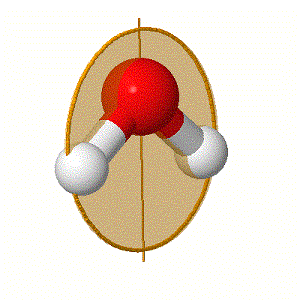
![]() – Plane of symmetry - can be described as horizontal (h) or vertical (v) in relation to the ‘proper axis of rotation’.
– Plane of symmetry - can be described as horizontal (h) or vertical (v) in relation to the ‘proper axis of rotation’.
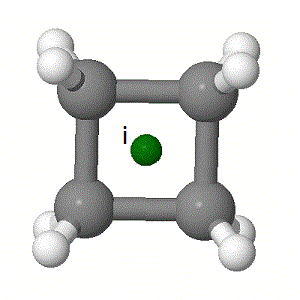
i – Centre of symmetry - also called the 'centre of inversion'. This is a specific point through which it is possible to project every other point in the structure to an equivalent position on the opposite side of the centre.
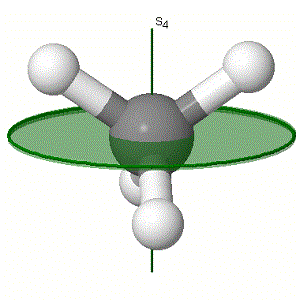
Sn – Rotation-reflection axis - also known as the 'improper axis of rotation'. The first stage is a rotation through 90° and then a reflection in the perpendicular plane (this does not have to be a plane of symmetry in the molecule).
E – The identity - This symmetry element is present in all shapes and is associated with leaving the object in an identical configuration to the starting point.
Below are some examples of these elements: