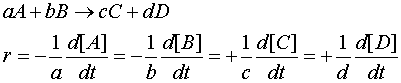 |
BASIC PRINCIPLES
Hint
For the general case :
Example :
For the reaction 2A → B, the rate of reaction can be expressed as:r = - ½d[A]/dt = + d[B]/dtNote : The -d[A]/dt term is multiplied by (1/2) since there are two A molecules as reactants, and the +d[B]/dt term is multiplied by (1/1) since there is one B molecule as a product.
Review Question
For the reaction NO + NO3 → 2NO2 , the rate of reaction can be expressed as
r = + d[NO]/dt = + d[NO3]/dt = - ½ d[NO2]/dtr = + d[NO]/dt = + d[NO3]/dt = - d[NO2]/dt
r = - d[NO]/dt = + d[NO3]/dt = + ½ d[NO2]/dt